Business
Hyperkalemia EKG Changes vs. Normal ECG: Critical Differences You Shouldn’t Ignore
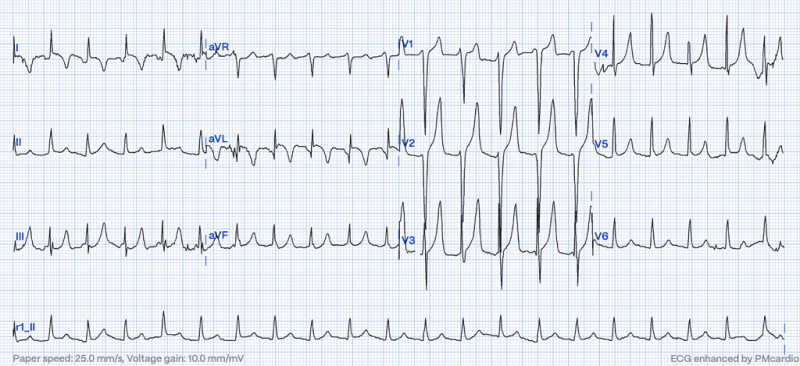
Hyperkalemia, defined as serum potassium levels exceeding 5.0 mEq/L, is a silent but deadly threat, making early recognition crucial in emergency medicine. One of the key ways to identify hyperkalemia is through electrocardiogram (EKG) changes. In this article, we will explore the critical differences between EKG changes in hyperkalemia and a normal ECG, highlighting why these differences should not be overlooked.
Understanding Hyperkalemia EKG Changes
When a patient presents with hyperkalemia, there are distinct EKG changes that can be observed. These changes are indicative of the effect that high levels of potassium have on the heart's electrical activity. Some common hyperkalemia ekg changes associated with hyperkalemia include:
- Peaked T waves: One of the hallmark signs of hyperkalemia is the presence of tall, peaked T waves on the EKG. These T waves are often described as looking like pointy tent-like structures and can indicate significant potassium disturbances in the body.
- Prolonged PR interval: Another EKG change seen in hyperkalemia is a prolonged PR interval. This represents delayed conduction of electrical impulses through the atria, which can lead to serious rhythm disturbances.
- Wide QRS complex: In severe cases of hyperkalemia, a wide QRS complex can be seen on the EKG. This is often a sign of profound impairment of the heart's ability to conduct electrical signals properly.
Contrasting Hyperkalemia EKG Changes with a Normal ECG
In contrast to the EKG changes seen in hyperkalemia, a normal ECG will exhibit different patterns and waveforms. A normal EKG typically shows:
- Normal T waves: In a normal EKG, the T waves will be relatively small and rounded, without the characteristic peaks seen in hyperkalemia.
- Standard PR interval: The PR interval in a normal EKG will fall within the expected range, indicating that the electrical conduction system of the heart is functioning correctly.
- Narrow QRS complex: A normal EKG will show a narrow QRS complex, demonstrating efficient conduction of electrical impulses through the heart's ventricles.
Why You Shouldn’t Ignore Hyperkalemia EKG Changes
Identifying and recognizing the EKG changes associated with hyperkalemia is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment. Failure to address hyperkalemia can lead to serious complications, including life-threatening arrhythmias and cardiac arrest. By understanding the critical differences between hyperkalemia EKG changes and a normal ECG, healthcare providers can initiate appropriate management strategies to prevent adverse outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyperkalemia EKG changes present distinct patterns on an electrocardiogram that differ significantly from a normal ECG. These changes, such as peaked T waves, prolonged PR intervals, and wide QRS complexes, serve as important indicators of potassium imbalance in the body. Recognizing these differences and acting promptly can make a significant difference in patient outcomes. Remember, when it comes to hyperkalemia, the EKG doesn’t lie – so pay attention to the subtle but critical changes it reveals.
Source:
Click for the: Full Story
You might like











 Close Menu
Close Menu