Health
Amniotic Wound Grafts: A Regenerative Solution for Advanced Wound Healing
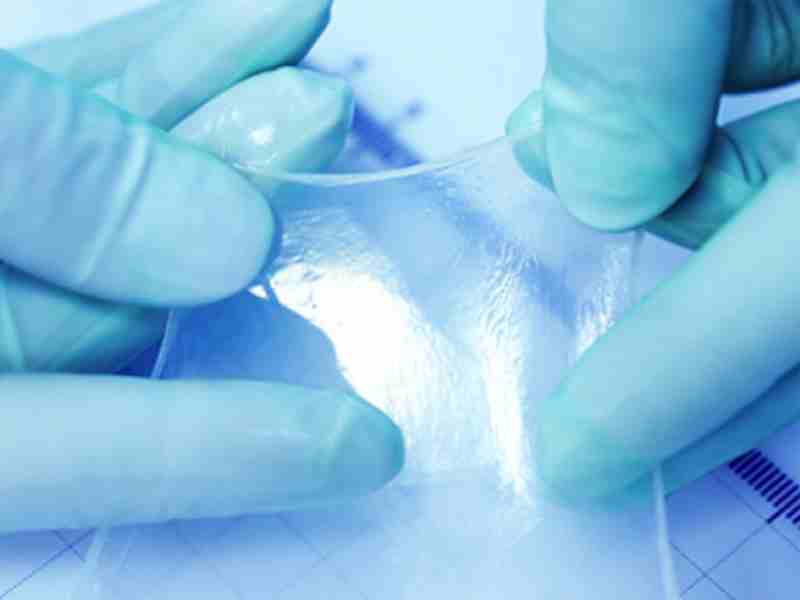
Wound healing is not always straightforward. For patients with chronic conditions, surgical wounds, or traumatic injuries, the body may struggle to repair damaged tissue on its own. In these cases, regenerative therapies are playing an increasingly important role in modern healthcare. One such therapy is amniotic wound grafts.
Used in hospitals, wound care centers, and specialty clinics, amniotic wound grafts help support the body’s natural healing process while reducing inflammation and protecting vulnerable tissue. This article explains what they are, how they work, and why they are becoming an important option in advanced wound care.
What Are Amniotic Wound Grafts?
Amniotic wound grafts are biologic grafts derived from the amniotic membrane, the thin inner layer of the placenta. This membrane surrounds and protects a baby during pregnancy and is naturally rich in healing components.
After healthy, full-term births, the amniotic tissue can be donated, screened, and processed under strict medical guidelines. Once preserved, it can be applied directly to wounds to support tissue repair and regeneration.
How Amniotic Wound Grafts Support Healing
The amniotic membrane contains a unique combination of growth factors, collagen, cytokines, and extracellular matrix proteins. These elements help regulate inflammation and encourage healthy tissue growth.
Amniotic wound grafts support healing by:
- Reducing inflammation at the wound site
- Promoting cell migration and tissue regeneration
- Providing a protective barrier against infection
- Maintaining a moist environment is ideal for wound healing
Unlike traditional dressings, these grafts actively participate in the healing process rather than simply covering the wound.
Common Clinical Applications
Amniotic wound grafts are used in a wide range of healthcare settings, particularly when wounds are slow to heal or at risk of complications.
Chronic Wounds
Patients with diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, or pressure injuries often benefit from amniotic grafts when standard wound care is not enough.
Surgical Wounds
After certain surgical procedures, amniotic wound grafts may be applied to support tissue repair and reduce excessive scarring.
Burns and Traumatic Injuries
In burn care and trauma cases, these grafts help protect exposed tissue, reduce pain, and support regeneration.
Complex or Non-Healing Wounds
When wounds fail to progress with conventional treatments, clinicians may use amniotic wound grafts as an advanced therapeutic option.
Benefits Compared to Traditional Wound Treatments
From a health care perspective, amniotic wound grafts offer several advantages over standard wound care methods.
Key benefits include:
- Faster healing in many patients
- Reduced inflammation and discomfort
- Lower risk of infection
- Minimal immune response
- Improved tissue quality and reduced scarring
These benefits make them particularly valuable for patients with underlying health conditions that interfere with normal wound healing.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
Amniotic wound grafts are considered safe when sourced and processed correctly. Donor tissue is thoroughly screened, and the grafts undergo sterilization and quality testing before clinical use.
Because the amniotic membrane is donated after childbirth and would otherwise be discarded, its use is widely regarded as ethical within the healthcare system.
Treatment decisions should always be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare provider who can assess individual needs and risks.
The Role of Amniotic Wound Grafts in Modern Healthcare
As healthcare increasingly focuses on regenerative and biologic solutions, amniotic wound grafts are becoming a valuable tool in advanced wound management. Rather than relying solely on synthetic materials or repeated interventions, clinicians are turning to biologic grafts that support natural healing.
By reducing inflammation and encouraging tissue regeneration, these grafts help improve outcomes for patients with difficult-to-heal wounds.
Final Thoughts
Amniotic wound grafts represent a significant advancement in modern wound care. Their regenerative properties make them an effective option for supporting healing in chronic, surgical, and complex wounds.
As research and clinical use continue to expand, amniotic wound grafts are likely to remain an important part of comprehensive, patient-centered health care.
Source:
Click for the: Full Story
You might like










 Close Menu
Close Menu